Hypoxia contributes significantly to the pathophysiology of major categories of human disease, including myocardial and cerebral ischemia, cancer, pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) is a nuclear protein involved in mammalian oxygen homeostasis. It is a heterodimer composed of HIF-1 alpha and HIF-1 beta subunits which are bHLH proteins of PAS (PER, ARNT, SIM) family. HIF-1 beta forms heterodimer with AHR, AHRR, HIF1 alpha and EPAS1/HIF2 alpha as well as with other bHLH proteins and its dimerization is required for efficient DNA binding.
HIF-1 beta is encoded by the ARNT (Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Nuclear Translocator) gene. It is able to partner with AhR to form a heterodimeric transcription factor complex which is required for AhR activity. This protein is required for the ligand-binding subunit to translocate from the cytosol to the nucleus after ligand binding. The complex then initiates transcription of genes involved in the activation of PAH pro-carcinogens. The heterodimer with HIF1A or EPAS1/HIF2A functions as a transcriptional regulator of the adaptive response to hypoxia.
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) is critically involved in cancer cell hypoxia adaptation, glycolysis, and angiogenesis. HIF-1 beta is associated with HIF-1 functions as a dimerization partner of HIF-1 alpha, and is on the other hand associated with carcinogenesis via dioxin signaling. A study using Novus' HIF-1 beta antibody (NB100-124) suggested that HIF-1alpha and beta share common signaling pathways for nuclear protein accumulation. Regulation of HIF-1beta protein expression was investigated in human prostate cancer (PCA) cells. (1)
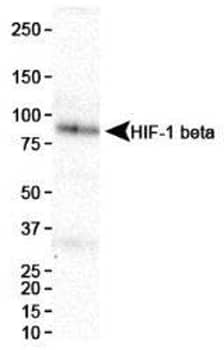
Western blot analysis showing HIF-1 beta expression in HeLa cell nuclear extracts using Mouse Anti-ARNT/HIF-1 beta Monoclonal Antibody (H1beta234) (Catalog #NB100-124).
The Ah receptor nuclear translocator protein (ARNT) is required for Ah receptor function. ARNT is shown to be a structural component of the XRE binding form of the Ah receptor. Furthermore, ARNT and the ligand-binding subunit of the receptor were extracted as a complex from the nuclei of cells treated with ligand. Arnt contains a basic helix-loop-helix motif, which may be responsible for interacting with both the XRE and the ligand-binding subunit. (2) Novus Biologicals offers HIF-1 beta reagents for your research needs including:
PMIDs: